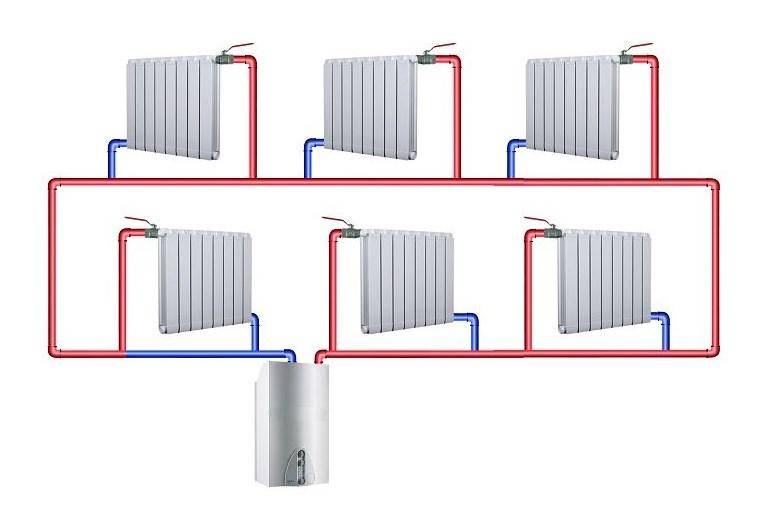
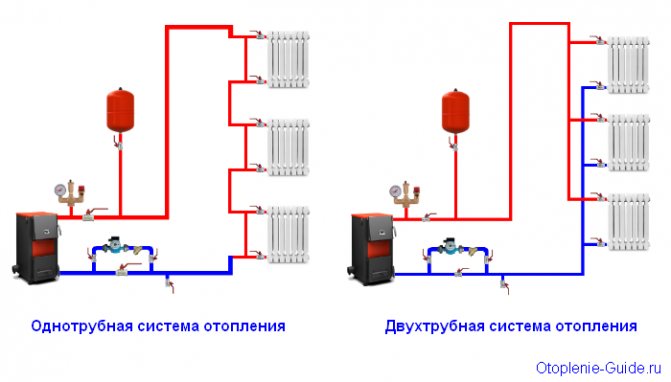
Two-pipe heating system
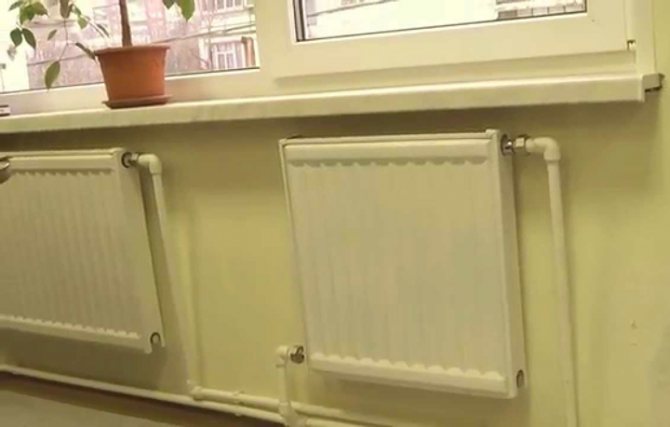
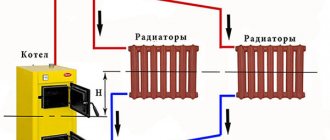
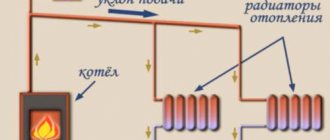
The principle of operation of a two-pipe heating system is somewhat different from that described above. In this case, the coolant rises along the riser and is supplied to each heating battery. And then, along the return line, it returns back to the pipeline, which transports it to the heating boiler.
With this scheme, the radiator is served by two pipes - supply and return, therefore the system is called two-pipe.
What are the benefits of this layout?
Two-pipe line
What can you expect by choosing this option for organizing heating of a private and residential apartment building?
- Such a system allows for uniform heating of each radiator. Any battery, no matter what floor it is on, receives hot water at the same temperature. If desired, a thermostat can be installed on the radiator, and then the weather in the house lends itself to self-regulation. The heat transfer of radiators installed in other apartments is not affected by the use of a thermostat in a single room.
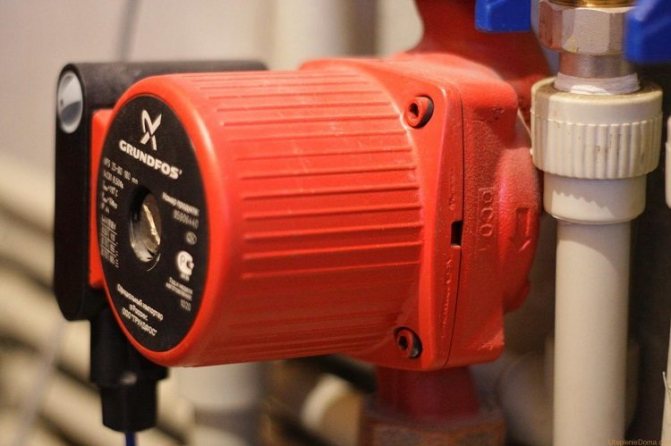
- In a two-pipe piping, there are no large pressure losses during the circulation of the coolant. Therefore, a powerful hydraulic pump is not needed for the normal functioning of the system. Water is able to circulate due to gravitational force, that is, by gravity. And if the water pressure is weak, it is enough to install a low-power pumping unit, which is more economical and easy to maintain.
- With the help of shut-off equipment, bypasses and valves, it is easy to organize such schemes that will allow you to repair one heating device, if necessary, without turning off all the heating of the house.
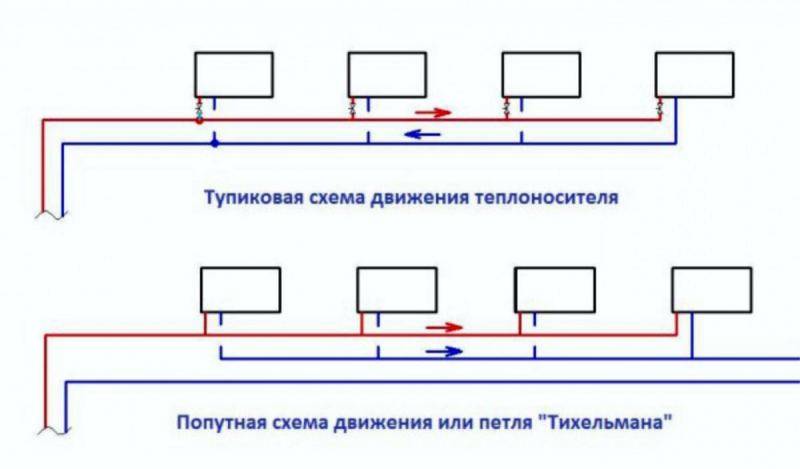
- Another additional bonus of two-pipe piping is the ability to use associated and dead-end hot water.
What is a passing scheme? This is when water flows both in the supply and in the return in the same direction. In a dead-end scheme, the supply and return water circulates in opposite directions. When driving along the way, provided that radiators of the same power are used, an ideal hydraulic balance is established. Therefore, it is not necessary to additionally use battery presetting valves.
If the heating devices have different power, you will have to calculate the heat loss of each, calculate and link the radiators using thermostatic valves. It is very difficult to do it yourself without knowledge and skills.
Note! Associated hydraulic gravity is used where long-distance pipelines are installed. For short systems, a dead-end scheme for the movement of the coolant is used
Classification of a two-pipe heating system
Types of systems
The classification of the two-pipe piping is made according to the location of the pipeline and the method of arranging the piping system.
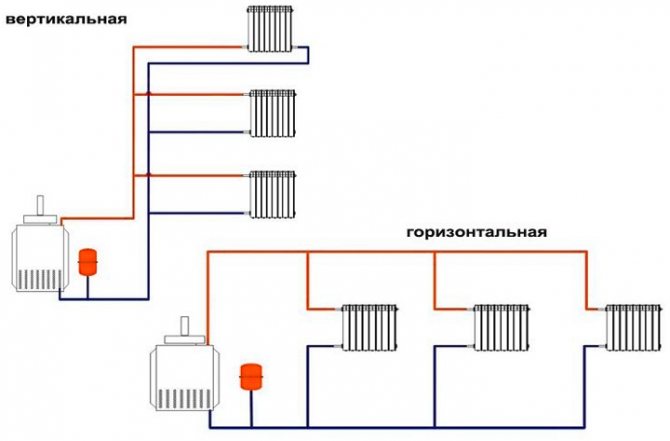
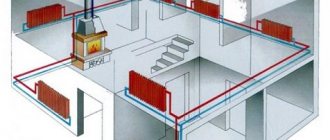
According to the location of the pipeline, it is divided into vertical and horizontal. In a vertical arrangement, all batteries are connected to a vertical riser. This option is most often used in apartment buildings. The main advantage of this connection is the absence of air congestion.
For a large private house, experts recommend choosing a horizontal two-pipe wiring and installing a Mayevsky crane in each radiator. It is needed to bleed air, and an example of its correct installation has been described in detail in previous articles more than once.
According to the wiring method, the two-pipe system can be with lower and upper piping.In this case, the hot water riser is placed in the basement or basement. The return line is located here, but is installed below the supply. All radiators are at the top. An upper air line is connected to the common circuit, which allows excess air to be removed from the system.
When installing the upper trim, the entire distribution line is mounted in the insulated attic of the building. An expansion tank is also installed there. You cannot use this scheme if you have a flat roof.
Disadvantages of a two-pipe system
Dual-circuit system
Comparing the two battery harness circuits, it is easy to conclude which one is better. The two-pipe system is much more efficient in any case. But it has one significant drawback. It will take twice as many pipes to assemble it. In addition, they come with a large number of fasteners, valves and fittings, so the installation of a two-pipe system is much more expensive.
Until recently, when steel pipes and labor-intensive welding processes were used to assemble a two-pipe piping, the amount was prohibitive. With the advent of metal-plastic and hot-brazing technology, the laying of a two-pipe line has become available to almost everyone.
Which system to choose
Summing up, we can conclude that for small one-story buildings, a one-pipe heating system is quite enough. This will provide more or less uniform heating and save a lot of time and money during construction.
For large buildings, consisting of a large number of rooms or several floors, it would be correct not to save money, but to prefer an energy efficient (albeit definitely more expensive and cumbersome) two-pipe heating system.
However, with the advent of metal-plastic and PVC pipes, when the pipes themselves have become relatively inexpensive, and the installation process is easy and simple, the issue of savings fades into the background, and the choice in favor of more efficient two-pipe heating systems becomes obvious.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: HDPE pipe for laying cables in the ground
Heating system options
The main criterion for separating all heating devices is the type of fuel. In addition, there are universal boilers operating on several types of fuel, which saves on electricity consumption. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the existing connection diagrams for various heating equipment.
- One-pipe. It is a simple option for laying a line for a coolant in a private and multi-storey building, as well as in an industrial enterprise. It is used in cases when it is necessary to lay a pipeline quickly and with minimal financial investment. The only caveat is the limitation of the length of the pipeline around the house to 30 m. There are three types of one-pipe connection scheme: horizontal, vertical and "Leningradka". They differ from each other in the way of supplying and removing the coolant to the batteries.
- Two-pipe. The batteries are connected to the supply line and return. This distributes heat more evenly throughout the building. Water is supplied to each heat exchanger at approximately the same temperature. A similar scheme is mainly used in multi-storey buildings with a large number of heated rooms. There are options for bottom and top connection.
- Radiation. From two collectors common for the floor, two pipes fit each of the radiators. The collectors themselves are connected to the common boiler equipment. With this scheme, you can connect not only batteries to heating, but also a "warm floor". The laying of the ray system must be performed even at the stage of building a house, since it will be extremely difficult to introduce it into an already finished building.

Which heating system is better
Which is better: one-pipe or two-pipe heating system, each user decides for himself. The choice depends on the type of housing and financial capabilities.
In addition, there is heating with natural and forced circulation. In the first case, water flows along the circuit under natural forces, in the second, thanks to the operation of the circulation pump.
One-pipe heating system
It works according to the principle: along one main pipe (riser), the coolant rises to the upper floor of the house (in the case of a multi-storey building); all heating devices are connected in series to the downstream. In this case, all the upper floors will be heated more intensively than the lower ones. It is a very common practice in Soviet-built multi-storey buildings, when it is very hot on the upper floors and cold on the lower ones. Private houses most often have 2-3 floors, so one-pipe heating does not threaten with a large contrast of temperatures on different floors. In a one-story building, heating is almost uniform.


Advantages of a one-pipe heating system:
hydrodynamic stability, ease of design and installation, low costs of materials and funds, since the installation of only one line for the coolant is required. The increased water pressure will ensure normal natural circulation. The use of antifreeze increases the efficiency of the system. And, although this is not the best example of a heating system, it has become very widespread in our country due to the high savings in material.
Disadvantages of a one-pipe heating system:
complex thermal and hydraulic calculation of the network; - it is difficult to eliminate errors in the calculations of heating devices; - the interdependence of the work of all network elements; - high hydrodynamic resistance; - a limited number of heating devices on one riser; - the inability to regulate the flow of the coolant into individual heating devices; - high heat loss.
Improvement of one-pipe heating systems
A technical solution has been developed to regulate the operation of individual heating devices connected to one pipe. Special closing sections - bypasses - are connected to the network. The bypass is a jumper in the form of a pipe segment that connects the direct pipe of the heating radiator and the return pipe. It is equipped with taps or valves. Bypass makes it possible to connect automatic thermostats to the radiator. This allows you to regulate the temperature of each battery and, if necessary, shut off the supply of coolant to any individual heating device. Thanks to this, individual devices can be repaired and replaced without completely shutting down the entire heating system. Correct connection of the bypass makes it possible to redirect the flow of the coolant through the riser, bypassing the element being replaced or repaired. For a high-quality installation of such devices, it is better to invite a specialist.

Vertical and horizontal riser diagram
According to the installation scheme, one-pipe heating is horizontal and vertical. A vertical riser is the connection of all heating devices in series from top to bottom. If the batteries are connected in series with each other throughout the floor, this is a horizontal riser. The disadvantage of both connections is the trapped air in radiators and pipes.

The heating system with one main riser is equipped with heating devices with increased reliability characteristics. All devices in a one-pipe system are designed for high temperatures and must withstand high pressures.
Installation technology of one-pipe heating system
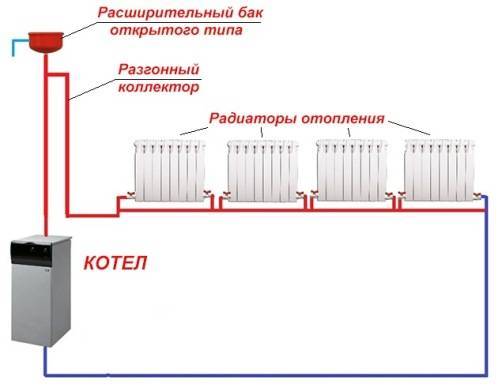
1. Installing the boiler at the selected location. It is better to use the services of a specialist from a service center if the boiler is under warranty. 2. Installation of the main pipeline.If an improved system is being installed, then the obligatory installation of tees at the points of connection of radiators and bypasses. For a heating system with natural circulation, when installing pipes, a slope of 3 - 5o per meter of length is created, for a system with forced circulation of a coolant - 1 cm per meter of length. 3. Installation of a circulation pump. The circulating pump is designed for temperatures up to 60 ° C, therefore it is installed in that part of the system where the lowest temperature is, that is, at the inlet of the return pipe to the boiler. The pump is running on the power supply. 4. Installation of the expansion tank. An open expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system, a closed one - more often next to the boiler. 5. Installation of radiators. They make a markup of places for installing radiators, fix the latter with brackets. At the same time, they comply with the recommendations of the manufacturers of devices for observing the distances from walls, window sills, floors. 6. Connect the radiators according to the selected scheme, installing Mayevsky taps (for airing the radiators), overlapping taps, plugs. 7. The system is pressurized (air or water is supplied to the system under pressure to check the quality of connection of all elements of the system). Only after that, a coolant is poured into the heating system and a test run of the system is carried out, the adjustment elements are adjusted.

For a one-story house
The simplest one-pipe heating scheme, which has been used by developers for more than half a century, is Leningradka.

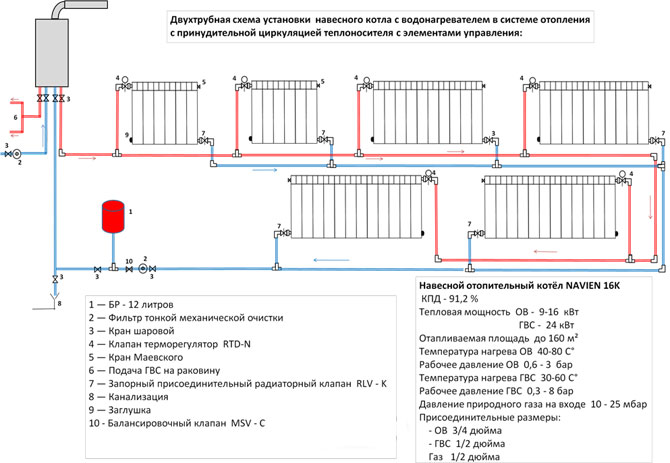
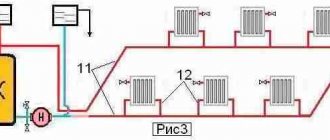
The figure shows a sketch of the modernized version of "Leningradka", with diagonal connection of radiators. The following elements are indicated in the figure (from left to right):
- Heating installation. For the implementation of this CO, boilers operating on solid fuel, gas (natural or liquefied) and electricity are suitable. Theoretically, liquid fuel boilers are also suitable, but the problem of storing fuel in a private house arises.
- The safety group, which consists of a blasting valve adjusted to a certain pressure in the system, an automatic air vent and a pressure gauge.
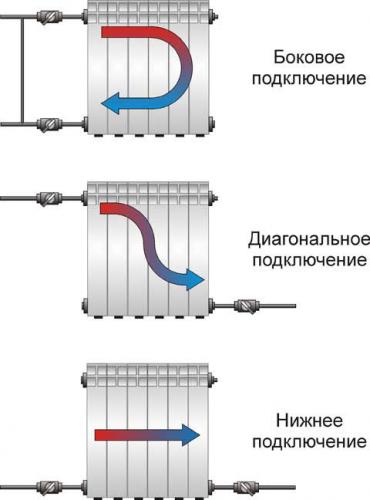
- Radiators connected to the system through shut-off ball valves. Needle balancing valves are installed in the bridge between the inlet and outlet of each radiator.
- A membrane expansion tank is installed on the return branch of the pipeline to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant.
- A circulation pump that creates a forced movement of the coolant through CO.
Now about what is not yet indicated in this sketch, but is a mandatory element for the reliable operation of this scheme. Above, only the pump was mentioned, but its piping was not indicated, which includes three ball stop valves, between which a coarse filter and a pump are installed. Quite often, a pumping group with a piping is included in the CO through a jumper, thereby forming a bypass.
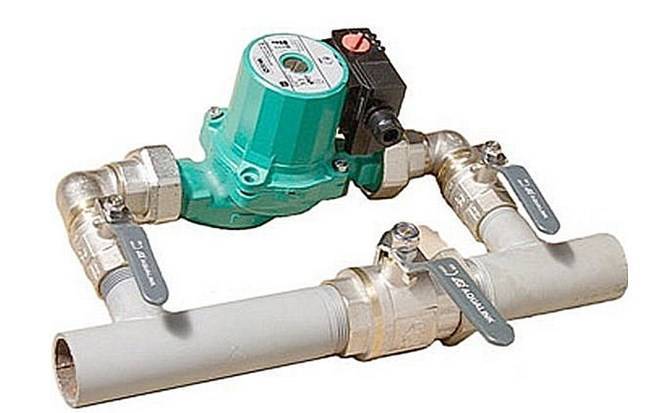


Often, developers ask if a bypass is needed in a one-pipe heating system? The thing is that this CO circuit is self-sufficient and efficient. But in the event of a power outage, the circulation pump will stop and the coolant will stop moving. The bypass is optional, but it is better to build it to switch from forced to natural circulation of the coolant in the event of an emergency.
As for the pipeline: since the temperature at the boiler outlet can reach 80 ° C, it is recommended to use reinforced polypropylene pipes of the required diameter for the Leningradka circuit. Why reinforced? The thing is that polymer pipes are quite cheap and practical, they are easy to install and they have a small mass. But, polymer pipes change their length when heated.Reinforced polymer does not suffer from such a "disease".
Advice: despite the fact that this CO option provides an automatic air vent, there are cases of airing the circuit. To solve this problem, it is recommended to use Mayevsky cranes on radiators.
Advantages of a one-pipe heating system and its disadvantages
For owners of small residential buildings, a one-pipe heating system looks tempting, especially if you pay attention to its following advantages:
- has stable hydrodynamics;
- convenience and simplicity of design and installation;
- small costs for equipment and materials.
The indirect advantages of a one-pipe system include the safety of supplying a coolant that diverges through the pipeline through natural circulation.
The most common problems that owners of a one-pipe heating system have to face include the following aspects:
- technical difficulties in eliminating miscalculations in the work made during the design;
- close interconnection of all elements;
- high hydrodynamic resistance of the system;
- technological limitations associated with the impossibility of self-regulation of the coolant flow rate.
Despite the listed disadvantages of this type of heating, a well-made heating system project will avoid many difficulties even at the installation stage. In view of the listed advantages and economic component, one-pipe schemes have become quite widespread. Both one-pipe and another type, two-pipe heating system have real advantages. What can you win and what can you lose by choosing one of the types for your home?
Pros and cons of a one-pipe system
To begin with, we recall that a one-pipe scheme is a single horizontal collector or a vertical riser, common to several radiators connected to it with both connections. The coolant, circulating through the main pipe, partially flows into the batteries, gives off heat and returns back to the same collector. A mixture of chilled and hot water with a temperature reduced by several degrees comes to the next radiator. And so on until the very last radiator.

The main difference between a one-pipe heating system and a two-pipe heating system, which gives it some advantage, is the lack of separation into supply and return pipelines. One line instead of two means less pipes and less work on their laying (punching walls and ceilings, fastening). In theory, the total cost should also be lower, but this is not always the case. Below we will explain why.
Thanks to the advent of modern fittings, it has become possible to regulate the heat transfer of each radiator in automatic mode. True, this requires special thermostats with increased flow area. But even they will not rid the system of its main drawback - the cooling of the coolant from the battery to the battery. As a result, the heat transfer of each subsequent device is reduced and it is necessary to increase its power by increasing the sections. And this is an increase in value.
If the line and supply to the device are of the same diameter, then the flow will be divided approximately equally. This cannot be allowed, the coolant will cool down strongly in the very first radiator. In order for a third of the flow to enter it, the size of the common collector must be made twice as large, and along the entire perimeter. Imagine if this is a two-storey house with an area of 100 m2 or more, where a DN25 or DN32 pipe is laid in a circle. This is the second increase in value.
If in a one-story private house it is necessary to ensure the natural circulation of water, then here a one-pipe heating system differs from a two-pipe one by the presence of a vertical booster header with a height of at least 2 m, installed immediately after the boiler. An exception is pumping systems with a wall-mounted boiler suspended at the required height.This is the third increase in value.

How to convert a one-pipe heating system into a two-pipe one?
Since the difference between one-pipe and two-pipe systems is the separation of the two streams, it is technically quite simple to carry out the conversion. It is necessary to lay a second pipeline along the existing pipeline, whose diameter can be taken 1 size smaller. The end of the old collector must be cut off near the last device and plugged, the remaining section up to the boiler must be connected to the new pipe.
You will get a scheme with a passing movement of water, only the coolant leaving the batteries needs to be sent to a new line. To do this, one supply section of each radiator will have to be reconnected from the old collector to the new one, as shown in the diagram:

It must be understood that in the process of alteration, you may encounter difficulties such as lack of space for a second pipe, the inability to punch a hole in the wall or ceiling, and so on. Therefore, before starting such a reconstruction, you need to think over everything well. It may be possible to establish the normal operation of the existing one-pipe system.
One-pipe heating system
This option is used in cases where it is necessary to carry out communications quickly and with minimal costs.

It is used in residential, private and industrial construction. A feature of this solution is the absence of a water return line. The batteries are connected in series, the assembly is carried out in a short time and does not require complex preliminary calculations.
How does a one-pipe line work
In such structures, the coolant is supplied to the upper point and flows downward, successively passing through the heating elements. When arranging a multi-storey building, it is practiced to install an intermediate pump, which creates the necessary pressure in the supply pipe to push hot water in a closed loop.
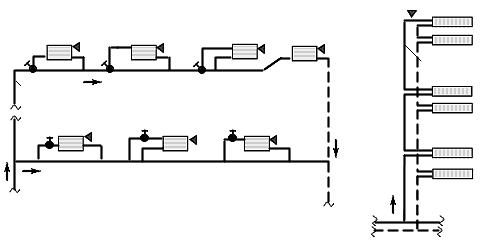
Vertical and horizontal schemes
The construction of a one-pipe line is carried out in a vertical and horizontal orientation. Vertical distribution is installed in buildings with two or more floors. The coolant is supplied to the radiators, starting from the topmost one. The horizontal heating main is most often used for the arrangement of single-level buildings - houses, summer cottages, warehouses, offices and other commercial facilities.
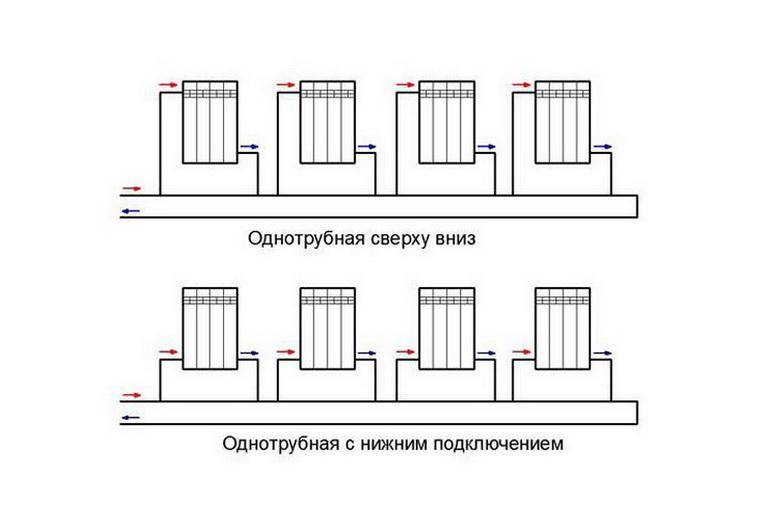

The layout of the pipeline assumes a horizontal arrangement of the riser with its sequential supply to the batteries.
Advantages and disadvantages
The single-pipe design of the heating main has the following advantages:
Installation is carried out quickly, which is important with modern requirements for the pace of construction. In addition, the appearance of a one-pipe collector with a height of several meters is superior to a complex system of two lines. Small budget. The cost estimate shows that the construction requires a minimum number of pipes, fittings and fittings. If consumers are installed on a bypass, then it becomes possible to regulate the heat balance separately in each room. The use of modern locking devices makes it possible to modernize and improve the line
This allows replacing radiators, inserting devices, and other improvements without a long shutdown of the system and draining water from it.
This design also has its drawbacks:
- The sequential arrangement of the batteries does not exclude the possibility of adjusting the heating temperature in them separately. This entails cooling all other radiators.
- Limited number of batteries on one line. It is impractical to put more than 10 of them, since at the lower levels the temperature will be below the permissible level.
- The need to install a pump. This event requires additional cash investments.The power plant can cause water hammer and damage to the lines.
- In a private house, you will need to install an expansion tank with a valve to bleed air. And this requires a place and carrying out insulation measures.
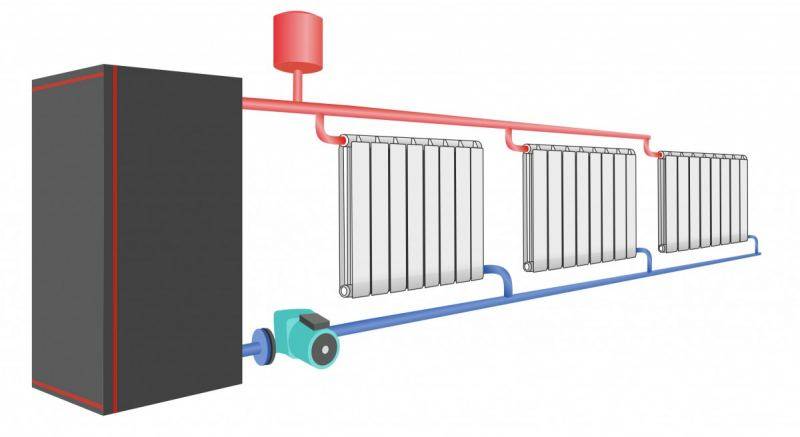
Dual-circuit heating system
Unlike a single-circuit system, two pipes are designed for the supply and return of the coolant. Such wiring is often used in new buildings and provides uniform heating of all rooms.


Which heating system is better
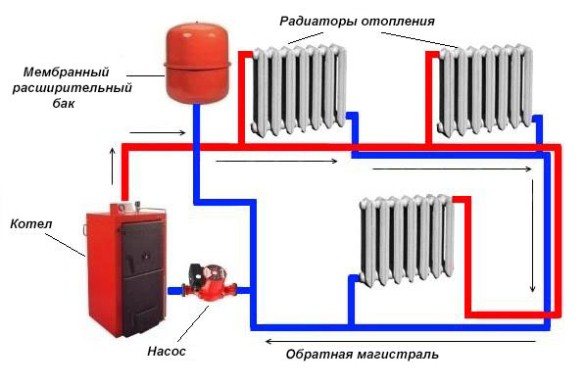
The principle of operation consists in the flow of water from the boiler to the batteries along one line. The supply pipe has a connecting inlet pipe through which the coolant enters each radiator. The end of the pipeline is located near the last battery. The second branch of the line is designed so that the already cooled water from the outgoing pipes, after passing through the entire chain, returns to the boiler. The circulation of the coolant occurs constantly while the heating is on.
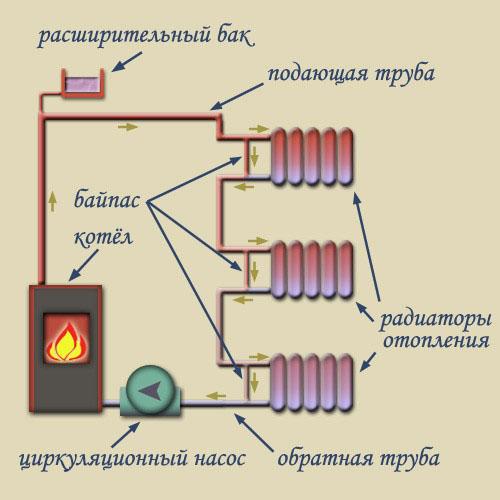
Double-circuit piping is possible in the upper and lower versions. In the first case, the system is set up in the attic or on the technical floor of the building. At the same time, an expansion tank is mounted, which must be insulated. They also install a boiler and a pump that supplies the coolant to the upper level. In the case of the lower wiring, the hot riser is located above the return one. The heating boiler is installed in the basement or on the ground floor with a recess below the floor. To bleed air from the radiators, the upper air line must be connected to the piping.
The advantages of a two-pipe connection scheme are as follows:
- simultaneous transfer of hot water to radiators allows you to adjust the temperature individually in each room and turn off the heating in those rooms that are not currently used;
- in the event of a breakdown, individual elements can be removed from the system and replaced without turning off the heating completely. This is possible thanks to ball valves, with the help of which the flow of water at the inlet and outlet of the radiator is shut off;
- a ready-made system can be supplemented with new batteries, both in horizontal and vertical design;
- less vulnerability and susceptibility to freezing.
The disadvantages of a two-circuit system are the higher cost of purchasing equipment and installing it in the house. But all of them fade into the background when frosts come, and in the house, due to the branching of the pipeline, the maximum accumulation of heat is possible.
What you need to consider when arranging any system
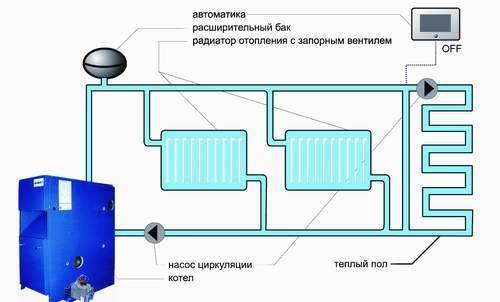

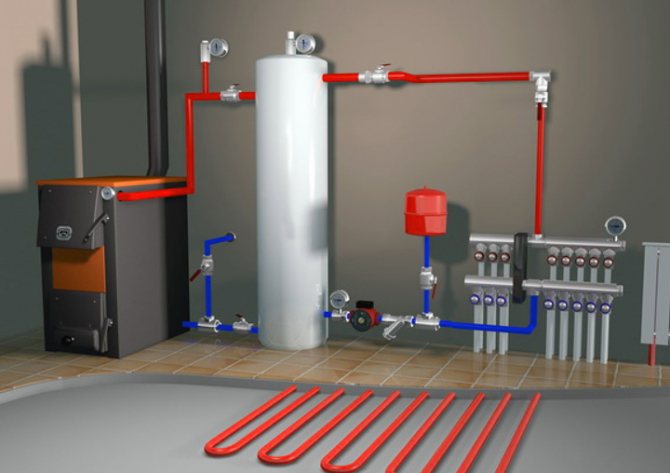
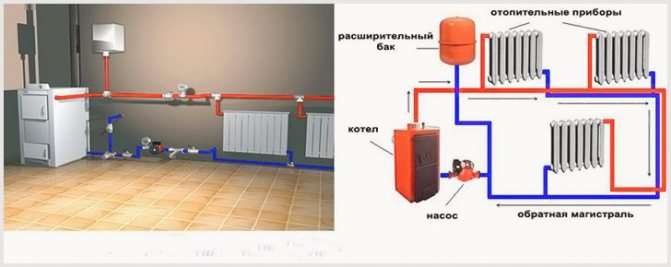
Heating boiler operation diagram.
It is important not to forget to install regulating thermococks at the inlet and outlet of the radiator, as well as a drain valve, which is usually located at the lowest point of the heating structure. The purchase of second-hand pipes and fittings or "cheap" in any heating system in the future can result in very serious problems that require major repairs not only of the entire heating structure, but also of the house itself due to a possible rupture of pipes with hot water and its flooding
The purchase of second-hand pipes and fittings or "cheaply" in any heating system in the future can result in very serious problems that require major repairs not only of the entire heating structure, but also of the house itself due to a possible rupture of pipes with hot water and its flooding.
Two-pipe heating distribution is possible for a private house with any number of floors. And its work can take place without using a circulation pump. But these systems have a rather low efficiency and in our time are already used by few people.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=IVHMLLJRL6M
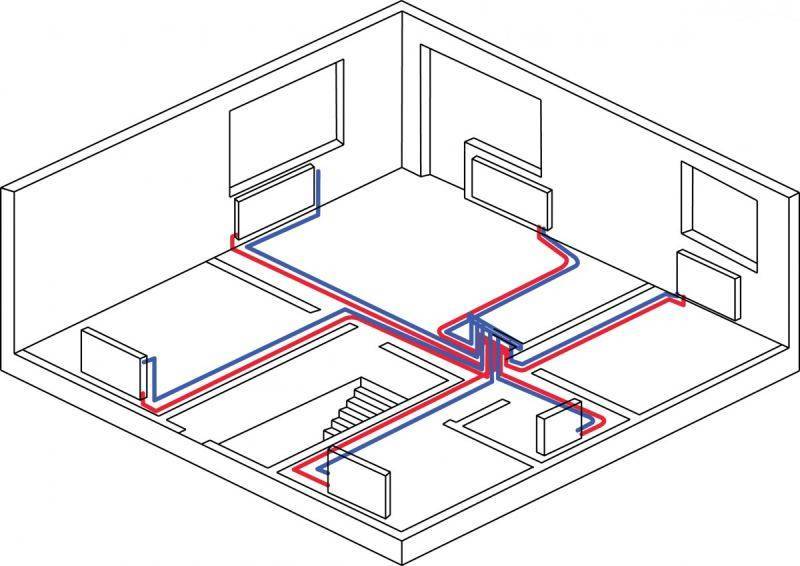
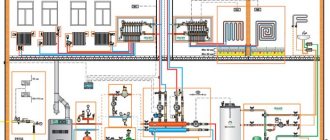
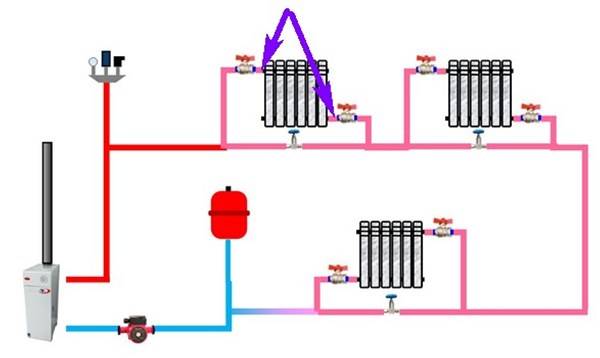
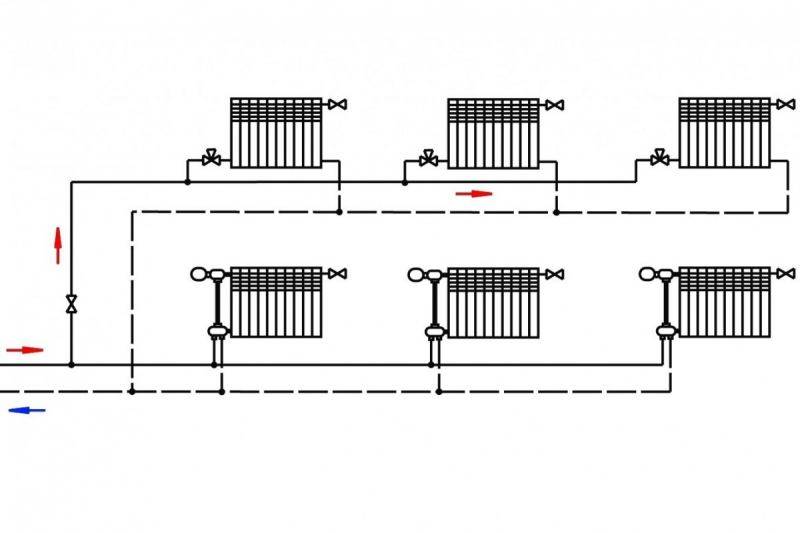
When deciding to place a two-pipe wiring in a house with a collector equipment, you need to carefully consider and plan the placement of the coolant distribution unit, the so-called comb.It will be correct to make the length of the pipes extending from it commensurate, since a significant difference in length from the comb to the radiators can lead to a significant difference in pressure. And this will complicate the adjustment of the system as a whole. The best solution in placing the comb is such that there will be approximately equal distance to each of the radiators from it.
Pipes for heating equipment can be copper, steel, polypropylene and metal-plastic, but in no case should you use galvanized pipes. The required type of pipes is selected depending on the construction project and with the preferred characteristics: economic, environmental. But the priority should be the hydraulic performance.
The flow rate of pipes required for laying this system will depend on the selected heating distribution scheme (two-pipe or one-pipe). Private houses with a large area require the equipment of a two-pipe system, into which a circulation pump is additionally cut in. Temperature control in each room is carried out using thermostats.
The principle of operation of the two-pipe system
Finding out how a one-pipe heating system differs from a two-pipe heating system, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the features of the second option. It is similar to the parallel connection of several pipes, which are bred using a special manifold system.
Pluses of two-pipe connection
Heating devices in such a network do not depend on the operation and characteristics of each other. The entire network is characterized by low hydrodynamic resistance, reliability, the ability to influence the temperature in each room.
Disadvantages of the system
A two-pipe heating system is much more complicated than a one-pipe heating system at the planning stage, and is also much more expensive. In addition, much more thorough validation and adjustment of all elements is required at startup. But the main drawback, of course, is the cost.
Advantages and disadvantages
The demand for a double-circuit heating system is explained by the presence of a number of significant advantages. First of all, it is preferable to a single-circuit one, since in the latter the coolant loses a noticeable part of the heat even before it enters the radiators. In addition, the double-circuit design is more versatile and suitable for houses of different storeys.
The disadvantage of a two-pipe system is its high price. However, many people mistakenly believe that the presence of 2 circuits implies the use of twice the number of pipes, and the cost of such a system is twice that of a single-pipe system. The fact is that for a single-pipe structure, it is necessary to take large-diameter pipes. This ensures the normal circulation of the coolant in the pipeline, and hence the efficient operation of such a structure. The advantage of a two-pipe one is that pipes of a smaller diameter are taken for its installation, which are much cheaper. Accordingly, additional elements (squeegees, valves, etc.) are also used with a smaller diameter, which also somewhat reduces the cost of the design.
The budget for installing a two-pipe system will not come out much more than for a one-pipe system. On the other hand, the efficiency of the former will be noticeably higher, which will be a good compensation.
What is the difference between a one-pipe heating system and a two-pipe heating system?
What is the difference between a one-pipe heating system
from a two-pipe heating system and which one is better to use for
heatingprivate house
? Kirov experts answer this question: each of the heating systems has its own advantages and disadvantages.
One-pipe heating system
Single-pipe is cheaper and easier to install: during installation, only one pipe is laid around the perimeter of the house. The whole procedure requires less time, therefore a one-pipe heating system is widely used for the installation and installation of utilities both in residential premises and at industrial facilities.In such a system, there is no riser for receiving and supplying hot water - waste heat carrier, which makes it possible to efficiently use the useful space of the building. Thanks to the use of modern building materials and technology, the one-pipe heating system has become the most popular heating system in the world.
The essence of this heating systems
consists in a series connection of radiators, which eliminates the installation of unnecessary pipes, in contrast to a two-pipe heating system, and reduces the total length of all pipes. However, a one-pipe heating system does not allow regulating the local heat transfer of each of them without consequences for the others. A weakening of the heating intensity on one of the radiators, for example, in one of the rooms, can lead to a weakening of the heating of subsequent radiators in other rooms. All this can lead to the cooling of the entire room, and all due to the fact that we have reduced the heating power in only one of the rooms! Thus, let us designate the first minus of a one-pipe heating system - each subsequent battery will always be colder than the previous one, since the coolant, in our case, hot water, will cool down as it passes through the radiators.
Maintaining a constant temperature in the heating system is not an idle question. Although for this they resort to various tricks - they install jumpers in order to maintain the same temperature between the floors of a multi-storey residential building and eliminate the possibility of a temperature difference between the radiators on the first and last floors.
Further, if you have a one-pipe heating system, be aware that hot water runs through the pipes under high pressure. Its acceleration requires powerful pumps, which inevitably entails higher operating costs. High pressure in pipes also means a greater risk of water leaks, accidents and repairs. Repairing the system will require stopping the movement of the coolant in the pipes. For comparison, let's say that a two-pipe system may not use water pumps, since the water in it can run by gravity, this is the first thing. And secondly, the repair of a certain section of the heating system will not require freezing the entire heating system in the house and shutting off the water in the pipes.
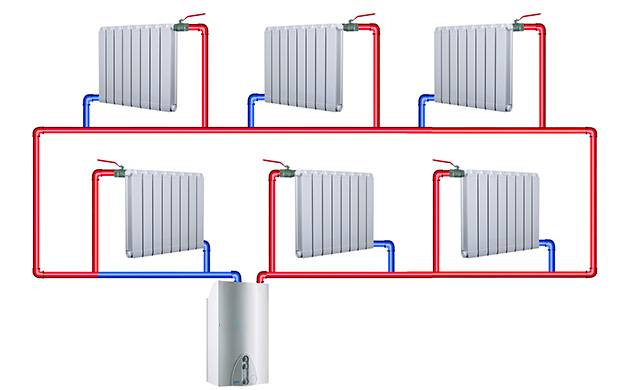
Two-pipe heating system
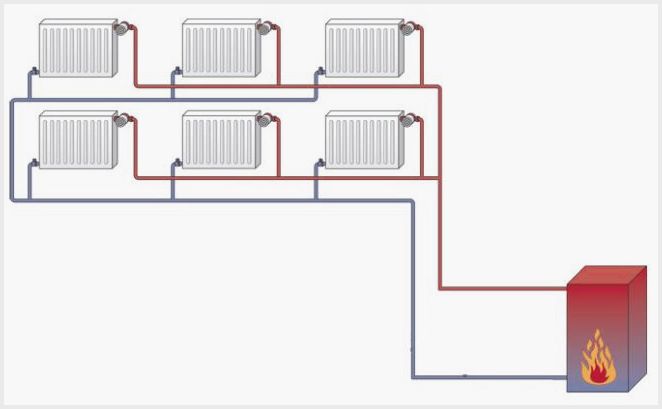
The two-pipe one is more expensive, more complicated, but the temperature in the radiators will be the same. This is achieved by the fact that a heat carrier with the same temperature throughout the room is supplied to each radiator from the heating boiler. The spent heat carrier (cooled water) is collected back into the pipeline, and the water flows back into the heating boiler, be it gas or electric. Two-pipe heating systems are used in multi-storey buildings when it is necessary to heat the entire room with one heating boiler.
As you have noticed, hot water of a certain temperature is supplied to each radiator, wherever they are installed in the house. By adjusting the heating temperature of each of the radiators in one of the rooms, we will not disturb the microclimate in other rooms of the house. This is a definite plus of a two-pipe heating system. This is achieved, in other words, by the fact that the radiators are not connected in series, as in a one-pipe heating system, but in parallel. Accordingly, the temperature of each battery can be adjusted separately and independently of the other batteries.
The circulation of water occurs due to the pressure drop in the pipelines. The heated water, having a low density, rushes upward, through pipes, through radiators, and emits its heat, and returns to the heating boiler through the pipeline, already cooled and with low density, by gravity. Although in some cases they resort to using circulation pumps. It is also worth noting that the installation of powerful pumps, unlike a one-pipe heating system, is not required.
Based on the design features of a two-pipe heating system, it becomes clear why more pipes are used in it than in a single-pipe one. The total number of pipes and their length are undoubtedly more than in a single-pipe system by about two times, therefore, the price of the system is higher.
Plumbing tips: what heating system to install in the house?
Which system to choose for yourself?
It is up to the owner to decide. If you have a one-story building (a house or cottage is not large in area), then the easiest way is to choose a one-pipe heating system, and not complicate your life with complex structures and engineering calculations. Single pipe
heating system
with a circular pump is enough to heat your home. Study the question whether or not it is worth changing the water in the heating system. We have prepared a separate material on this issue. If the area of your house is more than 150 square meters, then it is worth analyzing whether it will be comfortable in all rooms with a one-pipe heating system? Can then dwell on the choice of a two-pipe system? Specialists
LLC "GazTeploMontazh" Kirov
will help you with the choice and give you professional advice.
Natural circulation system
The principle of operation of this system is that the boiler heats the coolant, its density decreases with increasing temperature.


The cold heat carrier displaces the heated one upwards, it moves through the system, giving off heat, and then, having gained density, returns back to the boiler, etc.


In this way, the circulation of liquid through the system is carried out, accompanied by heating of the room, without a pump and other additional equipment.
An insignificant disadvantage is the small pressure drops in the system, this fact does not allow the system to be mounted on a large radius.

From the moment the boiler is turned on until the moment when the temperature in the room is fixed, a lot of time passes and this is a kind of disadvantage.


Another disadvantage is the condition of inclined installation of pipes, which is simply necessary in order for the liquid to move in the required direction.

A significant plus lies in the ability of the system to self-regulate - when the ambient temperature decreases, the circulation rate increases.

In addition to temperature, the following factors affect the speed of fluid movement: the radius of the pipes, the material from which they are made, their cross-section, the number of turns in the system, the presence of fittings and their type.


Heating two-pipe system

In this system, the heat carrier passes the heater cycle to the radiators and back.
In such a system, there are two pipelines: through the first, a hot heat carrier is supplied and divided, and through the second, the cooled liquid goes back to the boiler.
The system of two pipes is so divided into horizontal and vertical.
The advantages of the vertical system are that no air jams appear during operation, which, however, makes such a connection not cheap enough. With this system, each floor can be connected to an individual highway.


For large private houses, a horizontal heating system is very often used. Here the batteries are connected to a horizontal pipeline.
Air locks come out with air vents. This heating system is also divided into upper and lower wiring systems.
In a horizontal system with bottom piping, the heated piping is located in the basement, and the return riser is placed even lower.
In order to improve circulation, the boiler is installed below the level of the radiators, and in addition, a return riser is placed below the boiler. In order to remove air from the network, the upper air line is included in the circuit.
In a heating system with top wiring, the upper piping runs in the attic if the building has a sloping roof.
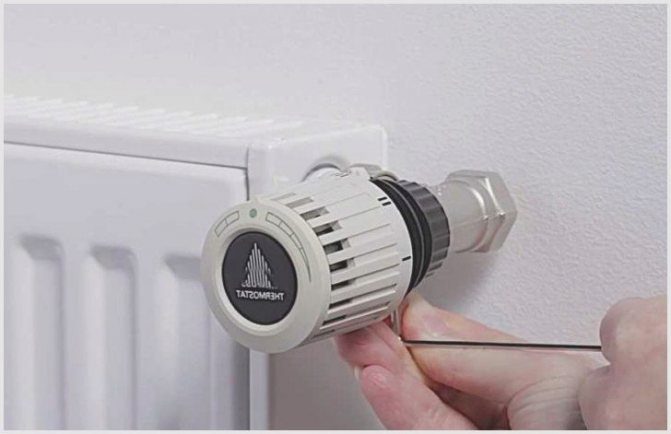


The advantage of a heating system with two pipes is the installation of heat supply auto-thermostats, which makes it possible to fully adjust the temperature in individual rooms.
This also includes the independence of the circuit devices, which is provided by a special collector system.
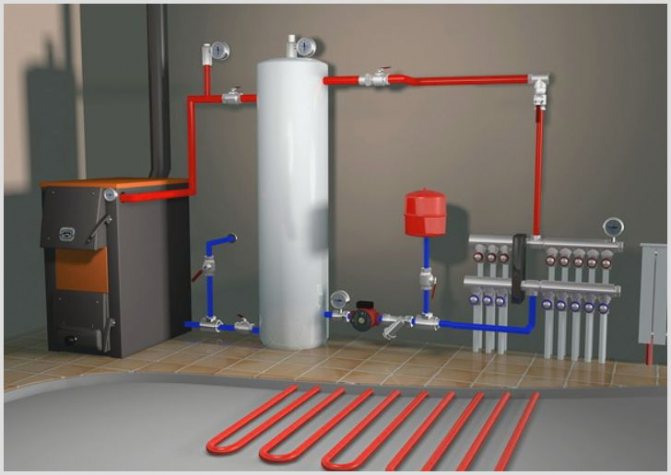


The difference between a two-pipe system and a system with one pipe is that in the first one it is possible to include additional batteries after connecting the key ones, and also the possibility of extension in horizontal and vertical directions.
Unlike one-pipe, here you can also easily correct possible errors.
The disadvantages of this system are minimal, if you have the necessary amount of financial resources and have the opportunity to call the wizard.
Installation of a heating system with a lower horizontal piping design

This system allows the open-type cistern to be located in a good warm place. Also, it is possible to connect the expansion and supply tanks, which enable you to use hot water directly from the very heating systems
.
In systems with forced circulation to reduce the flow rate of pipes, the outlet and supply risers are located at the level of the first.
- Downward angled connectors are installed on the boiler nozzles.


On the floor, under the walls, two branches of pipes are installed. One branch is connected to the boiler supply outlet, and the rest to the receiving outlet.
Tees are installed under each heating device, connecting them with pipes. The extension cistern is mounted at the top of the supply pipe. The pump is connected to the inlet of the heating tank, and the free end of the discharge pipe is connected to the pump.
Installation of a heating system with an upper horizontal wiring structure
The disadvantages of this system are that the extensive tank is placed outside a warm room on the ceiling.
- An angle connector is attached to the pipe segment leaving the boiler in order to turn the pipe upward.
- Using tees and corners, the upper branch is installed, and the tees are fixed above the heating devices.
- The tees are soldered to the upper section of the pipe, and a shut-off valve is placed at the point of intersection.
- After that, on the first floor, the lower branch of the outlet pipe is combined, which collects all pipes coming from the lower batteries.
- The free end of the outlet pipe is installed in the bypass, which is installed in the receiving pipe section.
Compared parameters
The following parameters will determine which heating system is better than one-pipe or two-pipe and in what situations one or another system should be used.
The cost
A one-pipe heating system is more expensive. The high cost consists of two main factors:
The need to increase the number of sections in each radiator next in the direction of coolant circulation. The one-pipe scheme consists of one supply pipeline, through which the coolant passes through the entire heating circuit, sequentially entering each heating device. From each radiator, the coolant comes out several degrees colder than when entering the radiator (part of the heat, about 10 ° C, is given to the room). Therefore, if a coolant with a temperature of 60 ° C enters the first radiator, then a coolant with a temperature of 50 ° C comes out of the radiator, then 2 flows are mixed in the supply line, as a result of which the coolant enters the second heating device with a temperature of about 55 ° C ... So there will be a loss of about 5 ° C after each radiator. It is to compensate for these losses that it is necessary to increase the number of sections for each subsequent heating device.

Which heating system is better one-pipe or two-pipe? What is the difference?
In a two-pipe scheme, there is no need to increase the number of radiator sections, sinceeach device receives a coolant of almost the same temperature. In the two-pipe there is both a supply and a return line, to which each heater is simultaneously connected. Having passed through the radiator, the coolant immediately enters the return line and is directed to the boiler for further heating. Thus, each radiator receives almost the same temperature (heat losses are present, but they are very insignificant).
Note! The best application for a one-pipe system is in small heating systems with no more than 5 radiators. With such a number of heating devices, the coolant, passing sequentially through all 5 radiators, does not lose heat in such critical quantities as in one-pipe systems with a large number of heating devices.
The need to use an enlarged supply pipeline. If the supply pipeline is too "thin", this will lead to the fact that many radiators simply will not get the heated coolant. A large-diameter pipe allows you to deliver the heated coolant to as many heating devices as possible. The thicker the supply pipe is, the fewer sections need to be added to each radiator.
Thus, an increase in the number of radiator sections and an increase in the diameter of the supply line makes a one-pipe system more expensive in comparison with a similar two-pipe system.
Profitability
The two-pipe scheme is more economical to operate. As noted above, in order to achieve uniform heating of all radiators in a one-pipe scheme, a "thick" feed is required, as well as an increase in the number of sections in radiators. All this increases the volume of the coolant, and the more coolant in the system, the more fuel is required to heat it. Therefore, to the question of which heating system is better than one-pipe or two-pipe from the point of view of efficiency, the answer will be in favor of a two-pipe system.
Installation process
A single tube is a more complex system in calculations, because it is necessary to correctly calculate how many sections should be increased for each subsequent heater
In addition, special attention must be paid to the calculation of the supply line and the radiator connection.
How does one-pipe heating work?
So, what is the difference between a one-pipe heating system and a two-pipe heating system? First of all, the principle of functioning. Only one main pipe is used here (it is also called a riser). The heated coolant rises along it, warming up the building, and all the batteries in the house are connected to the descending pipe.
Advantages of one pipe type
What is good about a one-pipe heating system? First of all, it requires the use of a much smaller amount of various materials for its creation and functioning. In addition, it is much more stable and stable in terms of hydrodynamics. It is easier not only to design it, but also to mount it; no special reconstructions are required in the existing infrastructure of the district. The great popularity of this system is due precisely to the fact that less materials are used for its construction. But from a technical point of view, this is far from ideal.
Disadvantages of the system
They are as powerful as the benefits.
- Hydraulic and temperature calculation for a one-pipe system is rather laborious and complex;
- If an inaccuracy has crept into the calculations, it will be very difficult to remove it in practice;
- All heating elements in the system are dependent on each other, and this must be taken into account;
- A limited number of heating devices can be installed on one riser;
- It is impossible to control batteries with regulators;
- If more than a dozen batteries are connected to a one-pipe system, then the temperature of the first radiator will be more than one hundred degrees, and the last will not even reach fifty;
- A single-pipe heating system requires the installation of special protective devices of increased reliability.
Improvement of one pipe system
In principle, it can be done so that the operation of each individual battery is regulated. To do this, you need to connect the closing sections to the network (experts call them bypasses), into which automatic thermostats for batteries are built. With their help, you can not only control all heating devices, but also completely cut off any of them from the water supply. That is, in the event of a breakdown, the battery can be removed and replaced with a new one without shutting off the entire heating system.
One-pipe heating system in a private house
If the building is one-story, this automatically removes many of the disadvantages of a one-pipe heating system, for example, uneven heating of floors. This is a multi-storey building on the upper floors will be the tropics, and on the lower ones it will be very cool. In a private house, there are usually no more than three floors, so the one-pipe system will work properly.
Installation of a one-pipe system


Installation pipeline the advanced system requires the installation of tees where bypasses and radiators are connected.
If this is a system with natural circulation, you need to create a slope with a length of 3-5 cm per one meter, and for forced circulation - 1 cm / m.


Circular pump installation - installed at the inlet of the return pipe to the boiler, since there is the lowest temperature.
Powered by power supply.


Installation of an expansion tank - a closed tank is usually installed next to the boiler. Open - at the highest point in the system.
Installation of radiators radiators are fixed with brackets and installed at the recommended distance from floors, walls and ceilings; for this, markings are made.


Connection is made according to the scheme, using valves for airing the radiators, which overlap the taps and plugs.
System pressure testing after which the coolant is poured into the battery and the system regulation is adjusted directly.